Embark on a captivating journey with our Biomolecules and Enzymes Practice Worksheet, an indispensable tool for unraveling the intricate world of these essential biological components. Prepare to delve into the depths of biomolecule structure, function, and classification, while simultaneously exploring the fascinating realm of enzyme action, kinetics, and regulation.
Through engaging questions and comprehensive answer keys, this worksheet empowers you to master the intricacies of biomolecules and enzymes, laying the foundation for a deeper understanding of cellular processes, biotechnology, and medicine.
Biomolecules
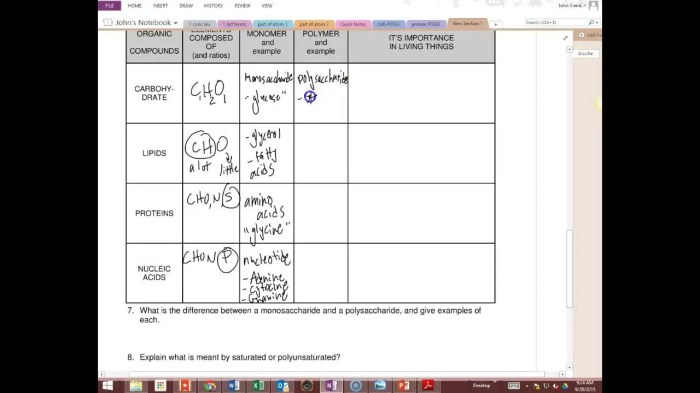
Biomolecules are organic compounds that are essential for life. They are the building blocks of cells and tissues, and they play a vital role in all cellular processes. Biomolecules can be classified into four main groups: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.Carbohydrates
are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They are the body’s main source of energy and can be classified as either simple or complex. Simple carbohydrates, such as glucose and fructose, are easily digested and provide a quick source of energy.
Complex carbohydrates, such as starch and cellulose, are more slowly digested and provide a sustained source of energy.Proteins are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. They are essential for building and repairing tissues, and they play a role in a variety of cellular processes, including metabolism, cell signaling, and immune function.
Proteins can be classified into two main groups: globular proteins and fibrous proteins. Globular proteins are soluble in water and have a spherical shape. Fibrous proteins are insoluble in water and have a long, thin shape.Lipids are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
They are insoluble in water and can be classified into two main groups: fats and oils. Fats are solid at room temperature, while oils are liquid at room temperature. Lipids are an important source of energy and can also be used to store vitamins and hormones.Nucleic
acids are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. They are essential for storing and transmitting genetic information. There are two main types of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA. DNA is found in the nucleus of cells and contains the instructions for making proteins.
RNA is found in the cytoplasm of cells and helps to translate the instructions in DNA into proteins.
Enzymes
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions. They speed up the rate of reactions without being consumed in the reaction. Enzymes are specific for their substrates, which are the molecules that they catalyze reactions for.The mechanism of enzyme action involves the formation of an enzyme-substrate complex.
The enzyme binds to the substrate, forming a complex. The enzyme then catalyzes the reaction, converting the substrate into products. The enzyme is then released from the products.Enzymes can be classified into six main groups: oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases.
Oxidoreductases catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions. Transferases catalyze the transfer of functional groups from one molecule to another. Hydrolases catalyze the hydrolysis of bonds. Lyases catalyze the cleavage of bonds without hydrolysis. Isomerases catalyze the isomerization of molecules.
Ligases catalyze the ligation of molecules.The activity of enzymes is affected by a number of factors, including temperature, pH, and the presence of inhibitors and activators. Temperature and pH can affect the conformation of the enzyme, which can in turn affect its activity.
Inhibitors are molecules that bind to enzymes and decrease their activity. Activators are molecules that bind to enzymes and increase their activity.
FAQ Compilation: Biomolecules And Enzymes Practice Worksheet
What are biomolecules and why are they important?
Biomolecules are the fundamental building blocks of living organisms, providing structure, energy, and carrying out essential functions. They include carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
How do enzymes facilitate biochemical reactions?
Enzymes act as catalysts, accelerating biochemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. They are highly specific, each enzyme recognizing and interacting with a particular substrate.
What factors can affect enzyme activity?
Enzyme activity can be influenced by factors such as temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and the presence of inhibitors or activators.