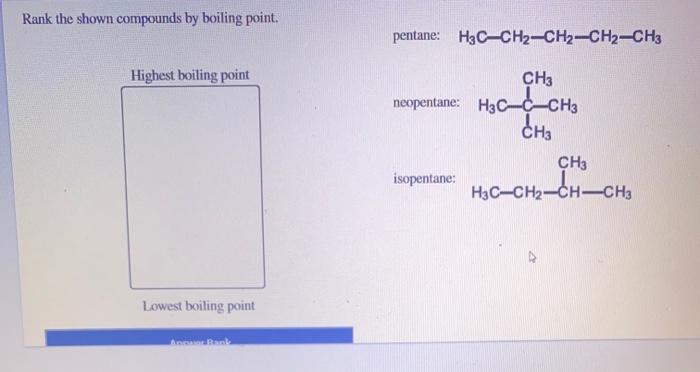
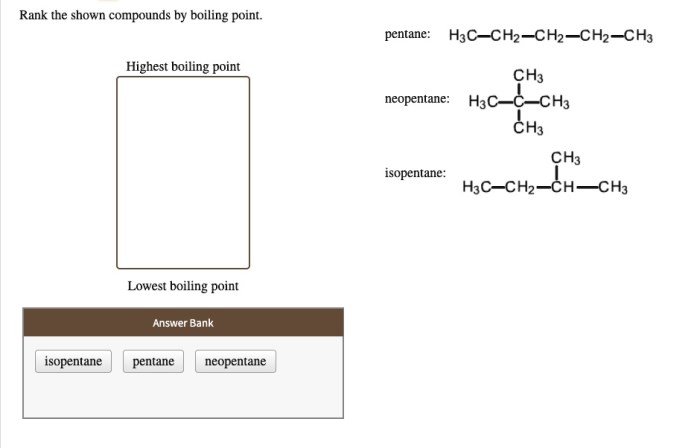
Rank the shown compounds by boiling point. This task requires a comprehensive understanding of the relationship between molecular structure and boiling point. Various factors influence a compound’s boiling point, including intermolecular forces, molecular weight, and polarity. By examining these factors, we can accurately rank the given compounds based on their boiling points.
The following paragraphs will delve into the characteristics of boiling point, the factors affecting it, and the applications of boiling point data in various fields. We will also provide a table ranking the given compounds by their boiling points.
Boiling Point Characteristics: Rank The Shown Compounds By Boiling Point.
Boiling point, the temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas, is a crucial property used to identify and separate compounds. It is influenced by various molecular factors and intermolecular interactions.
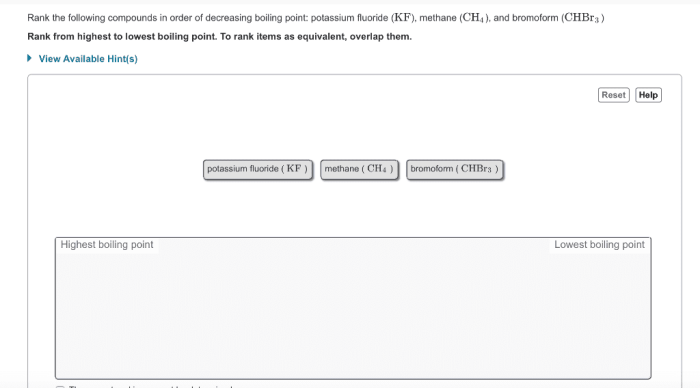
Compounds with stronger intermolecular forces have higher boiling points, as more energy is required to overcome these forces and transition into a gas.
Molecular weight also plays a role, with heavier molecules generally having higher boiling points due to their larger size and increased surface area for intermolecular interactions.
Polarity, the separation of electrical charges within a molecule, affects boiling point. Polar molecules have stronger intermolecular forces than nonpolar molecules, resulting in higher boiling points.
Ranking Compounds
| Compound Name | Molecular Formula | Boiling Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Water | H2O | 100 |
| Ethanol | C2H5OH | 78.3 |
| Methane | CH4 | -161.6 |
| Hexane | C6H14 | 68.7 |
Factors Affecting Boiling Point, Rank the shown compounds by boiling point.
- Intermolecular Forces:These include hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, and van der Waals forces.
- Molecular Weight:Heavier molecules tend to have higher boiling points due to increased intermolecular forces.
- Polarity:Polar molecules have stronger intermolecular forces than nonpolar molecules, leading to higher boiling points.
Applications of Boiling Point Data
- Compound Identification:Boiling point is a key parameter used to identify compounds by comparing it with known values.
- Separation Techniques:Distillation and fractional distillation rely on boiling point differences to separate compounds.
- Industrial Processes:Boiling point data is crucial for designing and optimizing industrial processes, such as refining petroleum and producing chemicals.
- Environmental Science:Boiling point information helps predict the fate and transport of chemicals in the environment, such as their volatility and potential for air pollution.
Q&A
What is the relationship between molecular structure and boiling point?
Compounds with stronger intermolecular forces have higher boiling points. Factors such as molecular weight, polarity, and shape influence the strength of these forces.
How can boiling point data be used in industry?
Boiling point data is crucial in refining petroleum, designing cooling systems, and optimizing chemical processes.