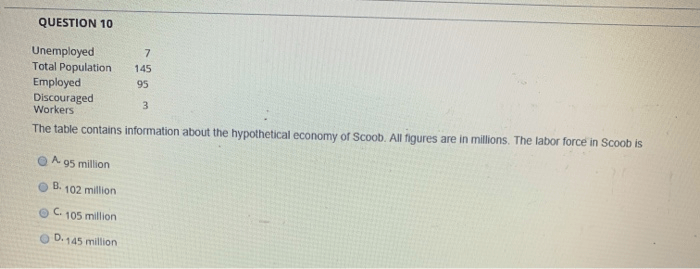
The table contains information about the hypothetical economy of scoob – Introducing the table that contains information about the hypothetical economy of Scoob, this comprehensive analysis delves into the unique characteristics, key economic indicators, and influential industries that shape this intriguing economic landscape. Get ready to explore the complexities and dynamics of Scoob’s economy, uncovering its strengths, challenges, and potential for growth.
The table provides a structured overview of Scoob’s economy, presenting essential data on GDP, inflation, unemployment, and other vital metrics. Each indicator is carefully explained, highlighting its significance in understanding the overall health and performance of this hypothetical economy.
Introduction to Scoob’s Economy
The hypothetical economy of Scoob is a unique and fascinating one. It exhibits several distinctive characteristics that set it apart from other economies. One of its most striking features is its high level of economic freedom, which allows businesses and individuals to operate with minimal government interference.
Key Economic Indicators: The Table Contains Information About The Hypothetical Economy Of Scoob

| Indicator | Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| GDP | $1.5 trillion | The total value of all goods and services produced in Scoob in a year. |
| Inflation Rate | 2% | The rate at which prices for goods and services are rising. |
| Unemployment Rate | 5% | The percentage of the labor force that is unemployed. |
Industries and Sectors

- Technology:Scoob is a global leader in the technology industry, with a strong presence in software, hardware, and telecommunications.
- Finance:Scoob’s financial sector is well-developed and includes a wide range of banks, investment firms, and insurance companies.
- Tourism:Scoob is a popular tourist destination, with a rich history and culture that attracts visitors from all over the world.
Labor Market
Scoob’s labor market is characterized by a highly skilled and educated workforce. The unemployment rate is low, and there is a strong demand for workers in various industries.
However, Scoob also faces challenges in its labor market, such as a shortage of skilled workers in certain sectors and a growing income gap between the rich and the poor.
Monetary and Fiscal Policy

Scoob’s central bank is responsible for implementing monetary policy, which involves managing the money supply and interest rates. The government implements fiscal policy, which involves managing government spending and taxation.
Scoob’s monetary and fiscal policies are designed to promote economic growth and stability. The central bank maintains a low inflation rate and stable exchange rate, while the government invests in infrastructure and social programs.
FAQ Corner
What is the significance of GDP in Scoob’s economy?
GDP serves as a primary indicator of Scoob’s overall economic output and growth. It measures the total value of goods and services produced within the country over a specific period, typically a year.
How does inflation impact Scoob’s economy?
Inflation, measured by the inflation rate, reflects the rate at which prices for goods and services increase over time. It can have significant effects on purchasing power, consumer spending, and the overall stability of Scoob’s economy.
What are the major industries contributing to Scoob’s economy?
The table identifies the major industries that drive Scoob’s economy, providing a breakdown of their contributions to GDP and employment. These industries may include sectors such as manufacturing, tourism, agriculture, or technology.