Embark on an intellectual journey with our comprehensive converse inverse contrapositive worksheet with answers. This invaluable resource delves into the intricacies of propositional logic, empowering you to master the art of deductive reasoning and enhance your critical thinking skills.
Through engaging exercises and detailed explanations, this worksheet unravels the fundamental concepts of inverse and contrapositive relationships, equipping you with a solid understanding of their applications and limitations. Prepare to embark on a transformative learning experience that will elevate your logical prowess to new heights.
Converse, Inverse, and Contrapositive Relationships: Converse Inverse Contrapositive Worksheet With Answers
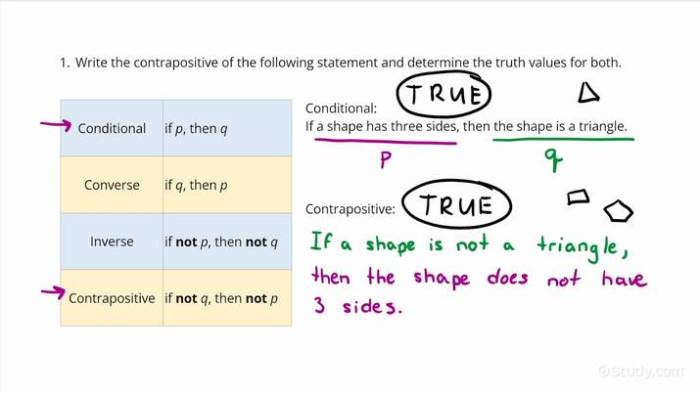
Propositional logic involves understanding the relationships between statements. Three important relationships are converse, inverse, and contrapositive. This article will explain these relationships, provide examples, and demonstrate how to analyze them using truth tables.
Inverse and Contrapositive Relationships, Converse inverse contrapositive worksheet with answers
Inverse
The inverse of a propositional statement negates both the hypothesis and conclusion. It is formed by switching the subject and predicate and negating both. For example, the inverse of “If it rains, the ground gets wet” is “If it does not rain, the ground does not get wet.”
Contrapositive
The contrapositive of a propositional statement negates the conclusion and keeps the hypothesis unchanged. It is formed by switching the subject and predicate and negating the conclusion. For example, the contrapositive of “If it rains, the ground gets wet” is “If the ground does not get wet, it does not rain.”
Converse and Inverse Relationships
Converse
The converse of a propositional statement switches the hypothesis and conclusion without negating either. It is formed by reversing the order of the subject and predicate. For example, the converse of “If it rains, the ground gets wet” is “If the ground gets wet, it rains.”
Difference between Converse and Inverse
The inverse negates both the hypothesis and conclusion, while the converse only switches their order. The inverse is logically equivalent to the original statement, but the converse is not necessarily equivalent.
Converse and Contrapositive Relationships
Difference between Converse and Contrapositive
The contrapositive negates the conclusion, while the converse does not. The contrapositive is logically equivalent to the original statement, but the converse is not necessarily equivalent.
Truth Table Analysis
A truth table can be used to analyze the relationships between the original statement, its inverse, converse, and contrapositive. The truth table shows the truth values of each statement for all possible combinations of truth values for the hypothesis and conclusion.
For example, the truth table for the statement “If it rains, the ground gets wet” is:
| Rains | Ground Wet | Original | Inverse | Converse | Contrapositive |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | T | T | T | T | T |
| T | F | F | T | F | F |
| F | T | F | F | T | T |
| F | F | T | T | F | T |
The truth table shows that the original statement, its inverse, and its contrapositive are all logically equivalent, meaning they have the same truth values for all possible combinations of truth values. However, the converse is not logically equivalent to the original statement.
Worksheet Exercises
Exercises
- Determine the inverse, converse, and contrapositive of the following statement: “If you study hard, you will pass the test.”
- Create a truth table to analyze the relationships between the original statement, its inverse, converse, and contrapositive.
Answer Key
- Inverse: “If you do not study hard, you will not pass the test.”Converse: “If you pass the test, you studied hard.”Contrapositive: “If you do not pass the test, you did not study hard.”
- Truth table:
Study Hard Pass Test Original Inverse Converse Contrapositive T T T T T T T F F T F F F T F F T T F F T T F T
FAQ Overview
What is the difference between converse and inverse relationships?
The converse of a propositional statement switches the hypothesis and conclusion, while the inverse negates both the hypothesis and conclusion.
How can I determine the validity of a converse or inverse relationship?
Construct a truth table to evaluate the truth values of the original statement and its converse or inverse. If the truth values are the same in all rows, the relationship is valid.
What are the applications of converse, inverse, and contrapositive relationships?
These relationships are essential in various fields, including mathematics, computer science, and law, where deductive reasoning plays a crucial role.
