Model code of ethics quiz gcu – Welcome to the Model Code of Ethics Quiz for GCU, a comprehensive resource designed to enhance your understanding of the ethical principles and guidelines that govern the counseling profession. Through engaging scenarios and thought-provoking questions, this quiz will equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate ethical challenges and make informed decisions in your counseling practice.
This quiz covers a wide range of topics, including the core principles of the Model Code of Ethics, the ethical decision-making process, counselor responsibilities, ethical boundaries, cultural considerations, legal and ethical issues, and professional development. By completing this quiz, you will gain a deeper understanding of the ethical obligations and best practices that guide ethical counseling.
Model Code of Ethics
The Model Code of Ethics (MCOE) is a comprehensive set of ethical principles and guidelines that guide the professional conduct of counselors. It provides a framework for ethical decision-making and helps ensure that counselors maintain high standards of practice.
Core Principles and Values
The MCOE is based on the following core principles and values:
- Autonomy and Self-Determination:Respecting the rights of clients to make their own decisions and live their lives according to their own values.
- Beneficence and Nonmaleficence:Acting in the best interests of clients and avoiding harm.
- Justice:Treating all clients fairly and equitably, regardless of their background or circumstances.
- Fidelity and Responsibility:Fulfilling commitments to clients and maintaining professional boundaries.
- Integrity:Acting ethically and honestly in all professional interactions.
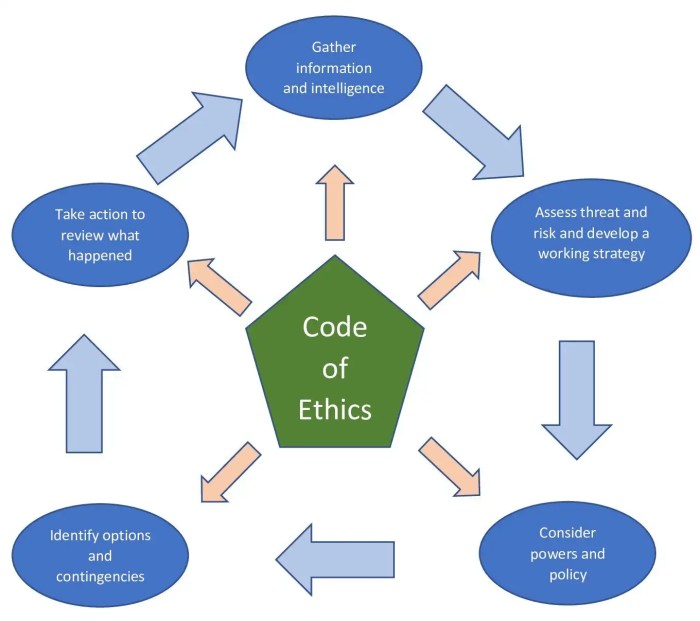
Ethical Decision-Making Process

The ethical decision-making process for counselors involves a systematic approach to addressing ethical dilemmas. It is guided by the Model Code of Ethics and helps counselors make informed and responsible decisions.
The steps in the ethical decision-making process include:
- Identify the ethical dilemma:Recognize the ethical issues involved in the situation.
- Gather relevant information:Collect information from various sources to understand the context and perspectives.
- Identify stakeholders:Determine who will be affected by the decision and consider their interests.
- Consult ethical guidelines:Refer to the Model Code of Ethics and other ethical resources for guidance.
- Consider alternative courses of action:Explore different options and their potential consequences.
- Weigh the consequences:Evaluate the potential benefits and harms of each option.
- Make a decision:Choose the course of action that aligns with ethical principles and minimizes harm.
- Document the decision:Keep a record of the decision-making process and the rationale behind it.
Using the Model Code of Ethics, counselors can navigate ethical dilemmas by:
- Referring to the ethical principles and standards for guidance.
- Seeking consultation with colleagues or supervisors.
- Utilizing ethical decision-making tools and resources.
Counselor Responsibilities
Counselors have ethical responsibilities towards their clients, colleagues, and the profession. These responsibilities include maintaining confidentiality, respecting diversity, and promoting client well-being.
Confidentiality
Counselors must maintain the confidentiality of their clients’ information. This means that they cannot share information about their clients with anyone else without their consent. There are a few exceptions to this rule, such as when the client is a danger to themselves or others, or when the counselor is required to report child abuse.
Respecting Diversity
Counselors must respect the diversity of their clients. This means that they must be aware of and sensitive to the different cultures, religions, and sexual orientations of their clients. Counselors must also be able to work with clients who have different abilities and disabilities.
The Model Code of Ethics Quiz GCU is a valuable resource for nursing students to test their understanding of ethical principles. For those seeking additional practice, the Bates Physical Exam Test Bank bates physical exam test bank offers a comprehensive collection of questions covering various aspects of physical assessment.
By utilizing both resources, students can enhance their preparation for ethical decision-making and develop a strong foundation in patient care.
Promoting Client Well-being
Counselors must promote the well-being of their clients. This means that they must help their clients to achieve their goals and to live happy and fulfilling lives. Counselors must also be aware of the potential risks of therapy and take steps to minimize these risks.
Ethical Boundaries
Counselors have an ethical responsibility to maintain appropriate boundaries in their relationships with clients. These boundaries help to protect both the counselor and the client from harm and exploitation. Failure to maintain appropriate boundaries can lead to a loss of trust, harm to the client, and even legal consequences.
There are a number of different types of ethical boundaries that counselors must adhere to, including:
Physical Boundaries
- Counselors must avoid any physical contact with clients that is not strictly necessary for the provision of services.
- Counselors must respect the client’s personal space and avoid any behavior that could be perceived as threatening or intimidating.
Emotional Boundaries
- Counselors must maintain a professional and objective stance with clients.
- Counselors must avoid becoming overly involved in the client’s personal life.
- Counselors must avoid any behavior that could be perceived as manipulative or exploitative.
Financial Boundaries
- Counselors must charge fair and reasonable fees for their services.
- Counselors must not accept gifts or other forms of compensation from clients that could compromise their professional judgment.
- Counselors must not engage in any financial transactions with clients that could be perceived as exploitative.
Sexual Boundaries
- Counselors must never engage in any sexual contact with clients.
- Counselors must avoid any behavior that could be perceived as sexually suggestive or inappropriate.
- Counselors must report any suspected sexual misconduct to the appropriate authorities.
Consequences of Boundary Violations
Violating ethical boundaries can have serious consequences for both the counselor and the client. For the counselor, boundary violations can lead to loss of licensure, loss of reputation, and even criminal charges. For the client, boundary violations can lead to harm, exploitation, and a loss of trust in the counseling profession.
How to Avoid Boundary Violations
There are a number of things that counselors can do to avoid boundary violations, including:
- Be aware of your own personal and professional needs.
- Set clear and appropriate boundaries with clients.
- Monitor your own behavior and be willing to make adjustments as needed.
- Seek consultation from a supervisor or colleague if you are unsure about whether or not your behavior is appropriate.
- Report any suspected boundary violations to the appropriate authorities.
By following these guidelines, counselors can help to ensure that they maintain appropriate boundaries in their relationships with clients and avoid the potential consequences of boundary violations.
Cultural Considerations
Cultural diversity significantly influences ethical decision-making in counseling. Counselors must be aware of their own cultural biases and values and how these may differ from those of their clients. They must also be able to adapt their counseling approach to meet the needs of clients from diverse cultural backgrounds.
Understanding Cultural Factors
Cultural factors that can influence the counseling relationship and ethical considerations include:
Values and beliefs
Cultural values and beliefs can shape a client’s worldview, including their views on mental health, help-seeking behavior, and the role of the counselor.
Communication styles
Different cultures have different communication styles, which can impact the counseling process. For example, some cultures may value direct communication, while others may prefer indirect or nonverbal communication.
Power dynamics
Cultural factors can also influence the power dynamics within the counseling relationship. For example, in some cultures, the counselor may be seen as an authority figure, while in others, the client may be seen as the expert on their own life.
Legal and Ethical Issues: Model Code Of Ethics Quiz Gcu
Counselors are bound by legal and ethical guidelines to protect clients’ well-being and ensure ethical practice.
Understanding the legal and ethical implications of counseling practice is essential for counselors to provide competent and ethical services.
Informed Consent
Informed consent is a process where clients are provided with clear and accurate information about the counseling process, including its goals, potential risks and benefits, and the counselor’s role.
- Clients must fully understand and voluntarily agree to the terms of counseling before services begin.
- Informed consent helps protect clients’ autonomy and rights.
Documentation
Counselors are required to maintain accurate and detailed documentation of client sessions.
- Documentation helps track client progress, justify treatment decisions, and provide evidence in legal proceedings.
- Counselors must balance the need for documentation with client confidentiality.
Reporting Requirements
Counselors have a legal and ethical obligation to report certain situations, such as:
- Suspected child abuse or neglect
- Threats of harm to self or others
- Impaired client functioning
Failure to report these situations can result in legal consequences and ethical violations.
Professional Development

Counselors have an ethical obligation to engage in ongoing professional development to maintain their competence and provide ethical services to clients. This includes continuing education, supervision, and self-reflection.Continuing education helps counselors stay up-to-date on new research, best practices, and ethical guidelines.
Supervision provides counselors with guidance and support from more experienced professionals, helping them identify and address ethical issues in their work. Self-reflection allows counselors to critically evaluate their own practice and identify areas for improvement.
Continuing Education
Counselors are required to complete a certain number of continuing education hours each year to maintain their license. These hours can be earned through workshops, conferences, online courses, and other educational activities. Continuing education helps counselors stay informed about the latest research and best practices in the field, as well as new ethical guidelines.
Supervision, Model code of ethics quiz gcu
Supervision is a relationship between a more experienced counselor (the supervisor) and a less experienced counselor (the supervisee). The supervisor provides guidance and support to the supervisee, helping them develop their skills and address ethical issues in their work. Supervision can be provided individually or in groups.
Self-Reflection
Self-reflection is an important part of ethical practice. Counselors should regularly reflect on their own practice, identifying areas for improvement and seeking out opportunities for professional development. Self-reflection can help counselors identify and address ethical issues in their work, as well as improve their overall effectiveness as counselors.
Ethical Challenges and Case Studies

Ethical challenges are inherent in the counseling profession, as counselors navigate complex situations involving client welfare, confidentiality, and professional boundaries. These challenges often require careful ethical decision-making to ensure the well-being of clients and maintain the integrity of the profession.
Case studies provide valuable insights into the ethical dilemmas counselors face and the decision-making process they employ to resolve them. By examining real-life scenarios, counselors can develop their ethical reasoning skills and learn from the experiences of others.
Case Study: Confidentiality and Dual Relationships
A counselor is treating a client who is struggling with depression and suicidal thoughts. The client discloses that they are in a romantic relationship with their supervisor. The counselor is concerned about the ethical implications of this dual relationship and the potential impact on the client’s therapy.
The counselor must weigh the client’s right to confidentiality against the ethical obligation to report the dual relationship. They must also consider the potential consequences of reporting, such as the impact on the client’s therapy and the supervisor’s reputation.
In this case, the counselor could consult with a supervisor or ethics committee to seek guidance and support in making an ethical decision. They may also consider terminating the therapeutic relationship to avoid any further conflicts of interest.
Case Study: Cultural Sensitivity and Bias
A counselor is working with a client from a different cultural background. The client presents with symptoms of anxiety and depression, but the counselor is not familiar with the cultural context that may be influencing the client’s experiences.
The counselor must be mindful of their own cultural biases and assumptions and seek to understand the client’s perspective. They may consult with other professionals who have experience working with clients from similar cultural backgrounds.
By being culturally sensitive and open to learning, the counselor can provide more effective and appropriate care to their client.
Case Study: Ethical Dilemmas in Group Therapy
A counselor is leading a group therapy session when one client discloses that they have been sexually abused by another client in the group. The counselor is faced with the ethical dilemma of how to handle this disclosure and protect the safety of all group members.
The counselor must consider the client’s right to confidentiality, the need to report the abuse, and the potential impact on the group dynamic. They may consult with a supervisor or ethics committee to seek guidance and support in making an ethical decision.
In this case, the counselor could choose to report the abuse to the appropriate authorities, while maintaining the confidentiality of the victim. They could also provide support and resources to the victim and facilitate a safe and supportive environment within the group.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the purpose of the Model Code of Ethics?
The Model Code of Ethics provides a framework for ethical decision-making in the counseling profession, ensuring that counselors maintain high standards of conduct and protect the well-being of their clients.
What are the core principles of the Model Code of Ethics?
The core principles of the Model Code of Ethics include beneficence, non-maleficence, autonomy, justice, fidelity, and veracity.
What are the steps involved in the ethical decision-making process?
The ethical decision-making process involves identifying the ethical issue, gathering relevant information, considering ethical principles and values, generating potential solutions, evaluating the consequences of each solution, and making a decision.